
John Miller
About the Author
John Miller, a 52-year-old man, who was working as a plumber for 20 years and had no hobby. But due to the Internet he found himself as a coin collector, he recognized how interesting it is. Of course he was scared to start a new passion, but now John can call himself an expert of numismatic pieces. It was surprising to learn what quarters are worth a lot of money when he first started collecting.
He organizes and attends many coin shows, and proves that nowadays there are no borders for knowledge.
Your Pocket Change Could Be Worth a Fortune
In 2024, a teenager in Georgia was having lunch money when she found a 1999 state quarter. She sold it for $10,000! It’s true that most quarters are only worth 25 cents. But some special quarters can be worth a lot more – even 400 times their original value! This happens because of mistakes made when they were produced, if they contain silver, or if only a few were made.
This guide will introduce the important dates for quarters made between 1965 and 2024.
Top 10 Most Valuable Quarters
Here is quarters worth money list by year:
| Year/Mint | Error Type | Value Range |
| 1932-D Washington | Low Mintage/Key Date | $100 – $10,000+ |
| 1965 Washington | No Silver | 25¢ – $10+ |
| 1976-S Bicentennial | Silver Content | $5 – $200+ |
| 1981-S Proof DCAM | Deep Cameo Finish | $10 – $100+ |
| 1999 Georgia | Die Break/”Extra” | $100 – $10,000+ |
| 1999-S Delaware Proof | Clear Finish | $1 – $100+ |
| 2004-D Wisconsin | Extra Leaf | $50 – $3,000+ |
| 2017-P Effigy Mounds | Die Gouge | $5 – $500+ |
| 2020-W V75 Privy | Privy Mark | $20 – $200+ |
| 2022-P Maya Angelou | Die Chip | $2 – $200+ |
What quarters are worth money may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors
1999 Georgia State Quarter
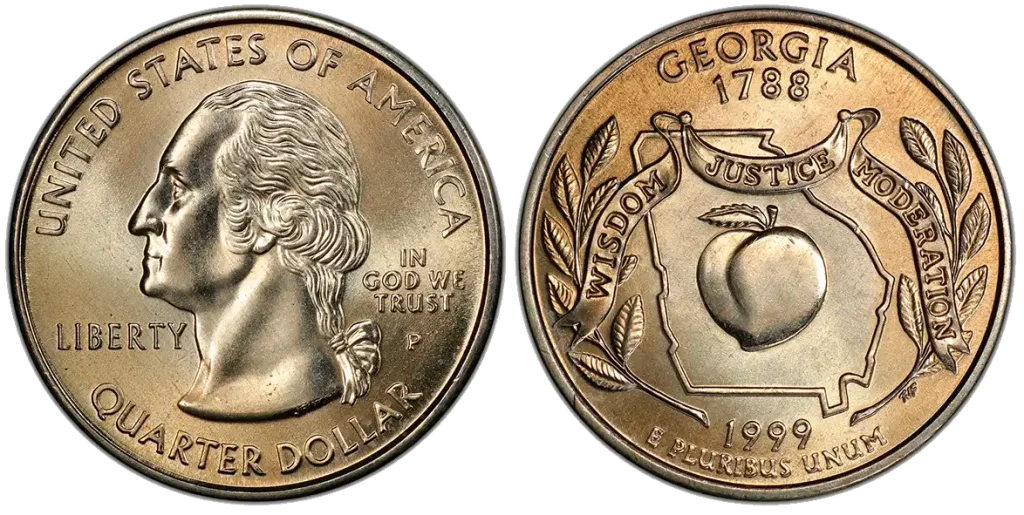

- Content: 91.67% Copper, 8.33% Nickel.
- Mintage: 1,154,340,000 (Philadelphia and Denver).
- Historical Context: This quarter is famous for a die break error. A small piece of the coin die broke off, creating an “extra leaf” on the ear of corn design.
2004-D Wisconsin Quarter
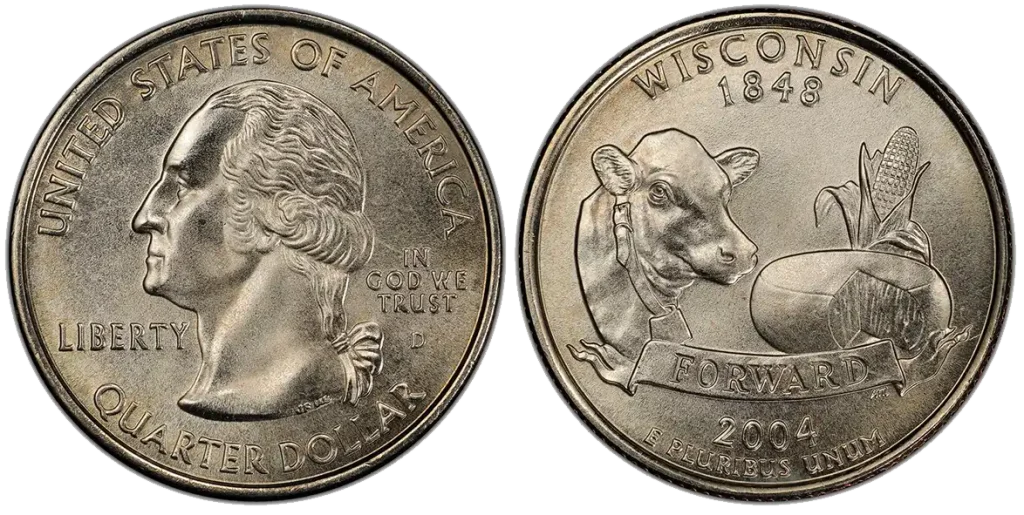

- Content: 91.67% Copper, 8.33% Nickel.
- Mintage: 453,200,000 (Denver).
- Historical Context: This coin also has an extra leaf error. It comes in two types: “Extra High Leaf” and “Extra Low Leaf.” This error happened because of a mistake during the coin’s production, causing an extra detail on the ear of corn. Finding a quarter worth money can be a real surprise in your daily change.
2020-W V75 Privy Quarter
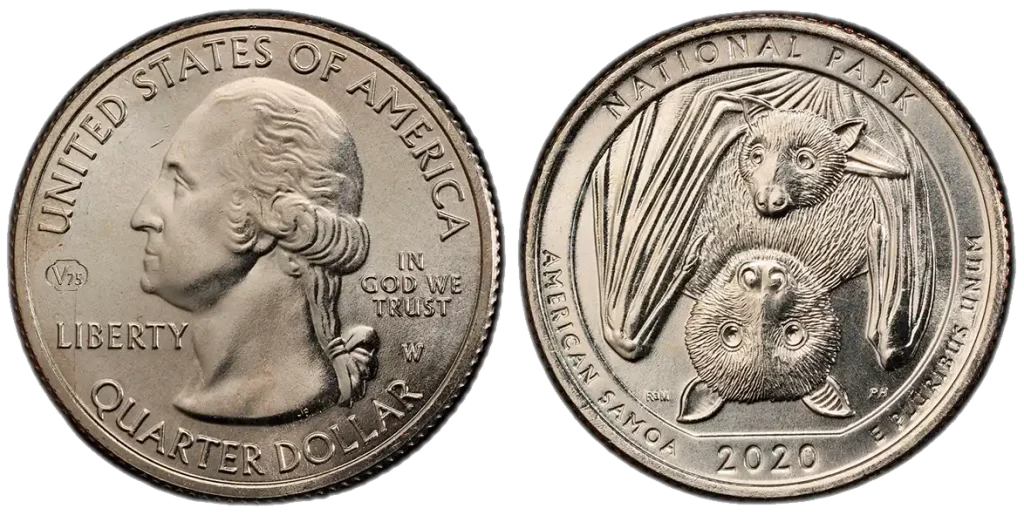

- Content: 91.67% Copper, 8.33% Nickel.
- Mintage: 2,000,000
- Historical Context: The bat is there on purpose to show the unique nature of the American Samoa National Park. The “V75 Privy Mark” is separate from the bat design; it’s a small mark on the front of the coin that celebrates the 75th anniversary of the end of World War II.
1965 Washington Quarter
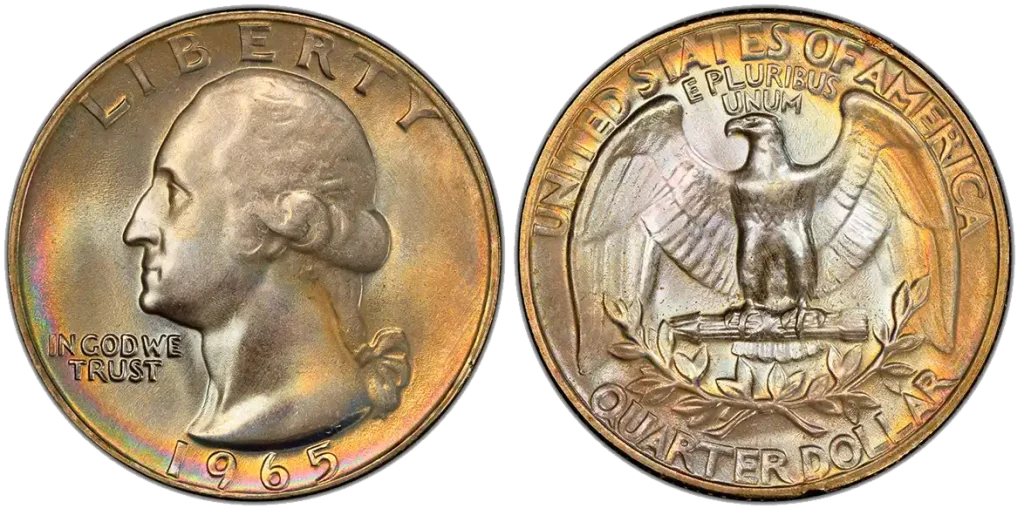

- Content: 75% Copper, 25% Nickel
- Mintage: 1,557,985,690 (Philadelphia and Denver).
- Historical Context: This coin marks a big change. Before 1965, quarters were made of 90% silver. From 1965 onwards, they switched to a copper-nickel blend. Finding a 1965 quarter that somehow got minted with silver content would be a very rare and valuable error. Most valuable 1965 quarters are simply due to their transitional nature, where a few silver planchets slipped into production.
1976-S Silver Bicentennial Quarter
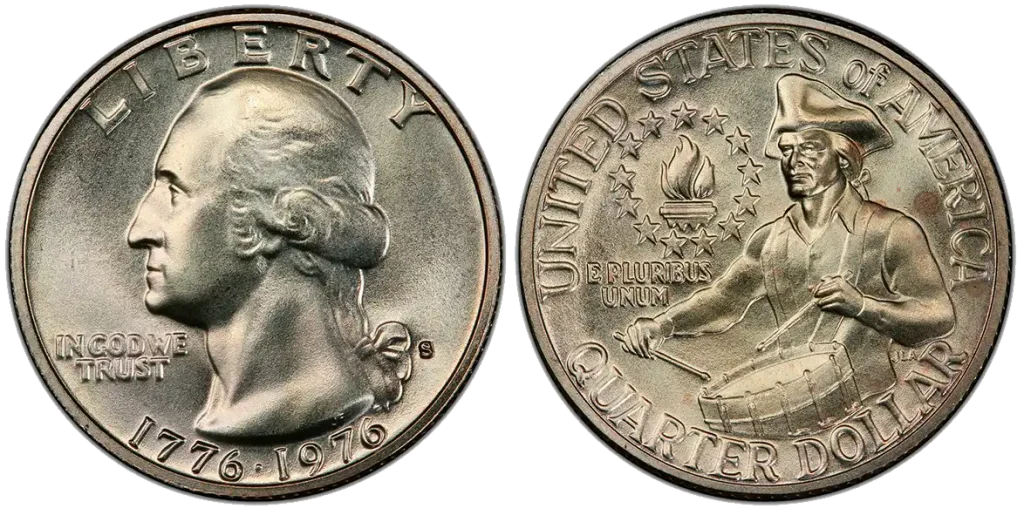

- Content: 80% Silver, 20% Copper for outer layers. 21% Silver, 79% Copper for core
- Mintage: 11,000,000 (San Francisco).
- Historical Context: This quarter was made to celebrate 200 years of American independence. Some of these were made for collectors in a special 40% silver proof version. This isn’t an error, but a special type of coin made with a more valuable metal.
1981-S Proof DCAM Quarter
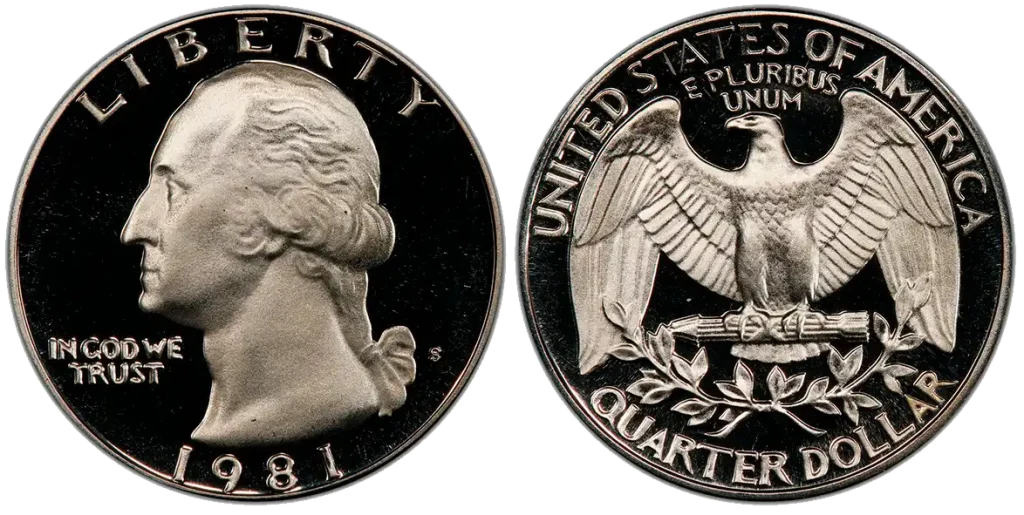

- Content: 91.67% Copper, 8.33% Nickel.
- Mintage: 4,063,083 (San Francisco Proofs).
- Historical Context: “DCAM” stands for “Deep Cameo.” Many US quarters worth money have special errors or low mintages.This refers to the special way the coin was made, with a very shiny, mirror-like background and frosted, detailed designs. It’s about the high quality of the strike rather than an error, making it very appealing to collectors.
1999-S Delaware Proof Quarter
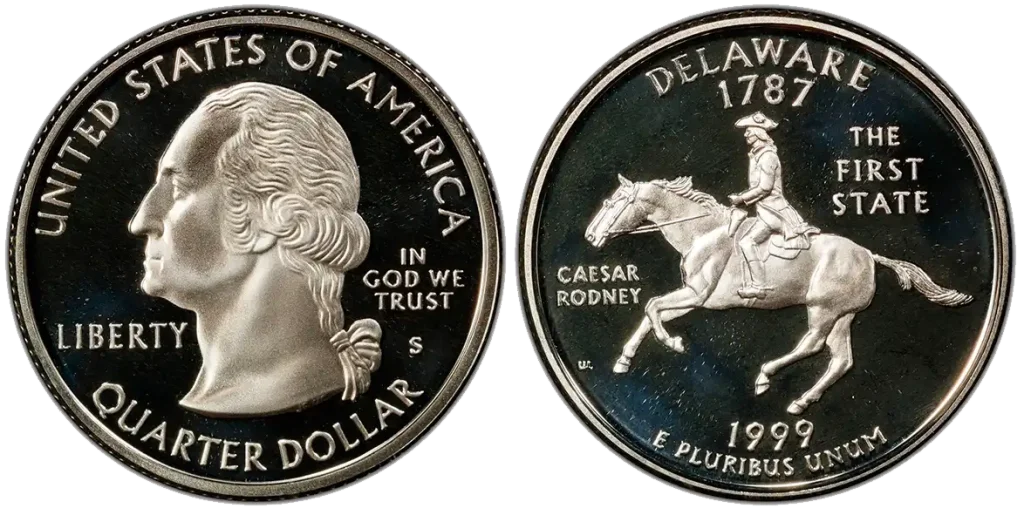

- Content: 91.67% Copper, 8.33% Nickel.
- Mintage: 804,500 (San Francisco Proofs).
- Historical Context: This was one of the first state quarters. “Proof” means it was made especially for collectors with a high-quality strike, often with a shiny background and frosted details. Similar to the DCAM, its value comes from its high quality of strike and limited mintage for collectors.
2017-P Effigy Mounds Quarter
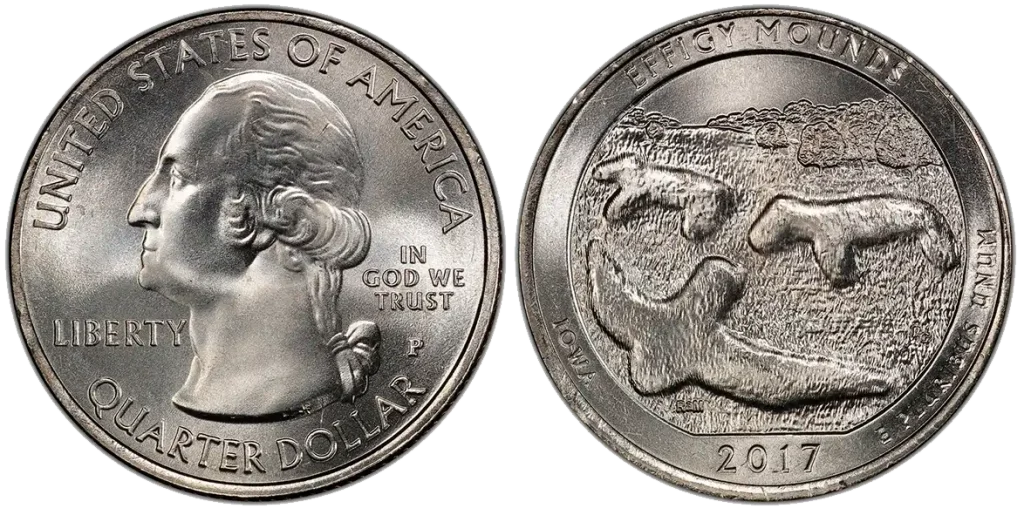
- Content: 91.67% Copper, 8.33% Nickel.
- Mintage: 206,400,000 (Philadelphia Mint).
- Historical Context: It depicts an aerial view of mounds in the Marching Bear Group at Effigy Mounds National Monument in Iowa.These mounds were built long ago by Native Americans, often for burial or ceremonial purposes, and some were shaped like animals or birds, which are called “effigy mounds.”
This coin can have a doubled die obverse error. This means parts of the front design look slightly blurry or doubled because the die that stamped the coin had a small error.
2022-P Maya Angelou Quarter
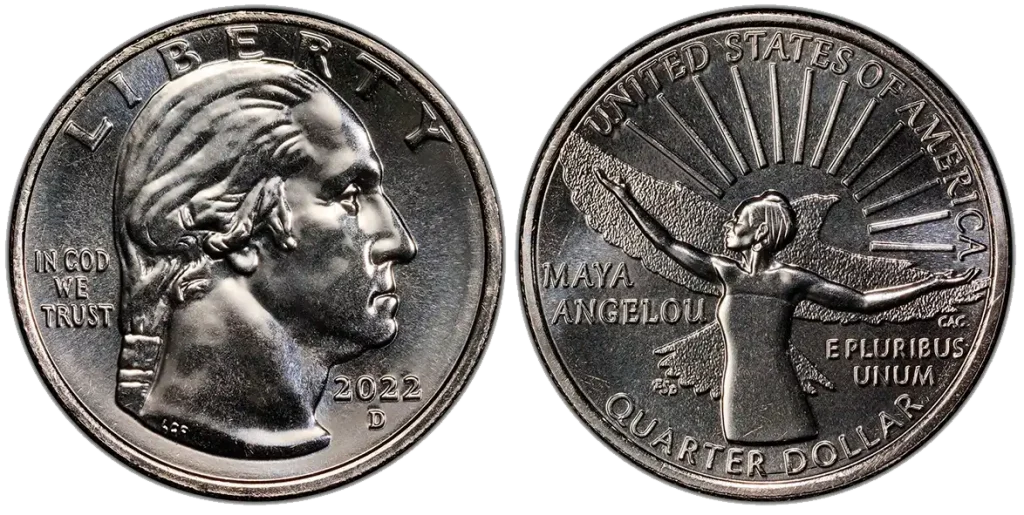

- Content: 91.67% Copper, 8.33% Nickel.
- Mintage: 300,000,000 (Philadelphia Mint).
- Historical Context: The 2022-P Maya Angelou Quarter is part of the American Women Quarters Program. This program celebrates important women who have made a big difference in American history.
Even some new quarters worth money can be found if they have rare errors or special marks.This quarter is known to have die crack errors. A small crack appeared on the metal die used to stamp the coin, which then left a raised line or mark on the coin itself. This is a common type of mint error.
1932-D Washington Quarter
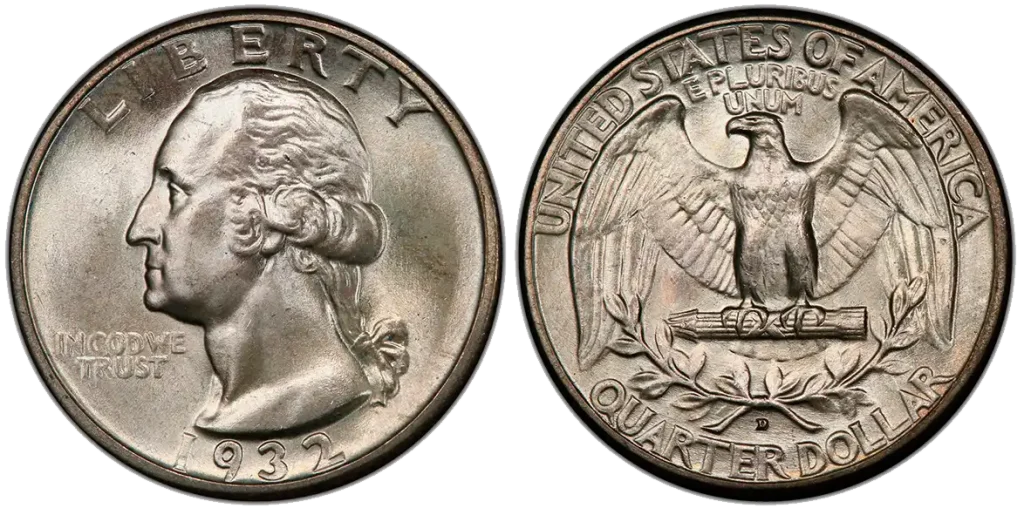

- Content: 90% Silver, 10% Copper.
- Mintage: 436,800 (Denver Mint).
- Historical Context: This is a “key date” coin because very few were made, especially at the Denver Mint. Its high value comes from its low mintage and its age, making it hard to find for collectors. It’s not an error coin but rare due to production numbers.
Critical Identification Factors
- Mint Marks Matter
W (West Point) and S (San Francisco) coins are often worth more money. The West Point mint makes fewer coins for general use. For example, in 2020 only 2 million W quarters were made. But the Philadelphia (No mark) and Denver (D) mints made over 3.5 billion quarters that year.
This makes the W coins much rarer and more valuable. S coins are usually for special collector sets called “proof” coins, which are also often worth more.
- Silver vs. Clad Coins
When discussing collectible coins, people often ask how much is a quarter dollar worth beyond its face value. Quarters made before 1965 are special because they are 90% silver. This means the metal itself is worth money, usually between $4 and $7, even if the coin is worn. You can check it by their sound when dropped.
For quarters made between 1965 and 1970, look for errors where a silver coin might have been accidentally made. These ones are very rare, but transitional silver errors can be worth a lot.
- Grade Determines Value
Coins in perfect condition like MS/PR-70 can be worth 100 times more than coins that have been used. “MS” means “Mint State” for regular coins, and “PR” means “Proof” for collector coins. A grade of 70 means the coin with no flaws is perfect. You never know the real value of change in your pocket, so it’s always smart to know how much is my quarter worth.
To know the true grade of a coin, it’s best to check them vie the top coin grading companies. These are PCGS, NGC, and ANACS. They are trusted experts who will carefully check your coin and give it a professional grade.
Spotting Money-Making Errors
This list of quarters worth money includes detailed descriptions of each valuable coin:
2004-D Wisconsin Quarter: “Extra Leaf” Varieties
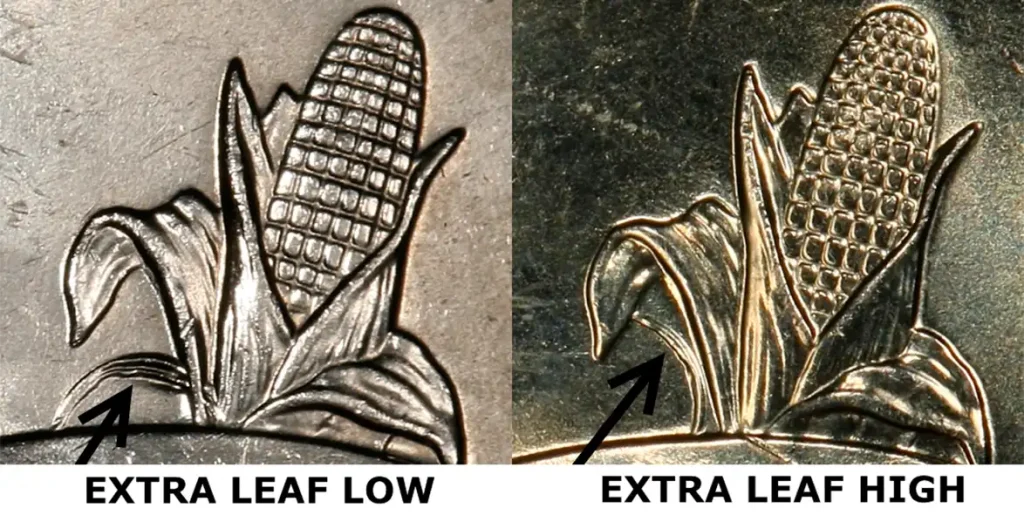

Finding error quarters worth money is often the dream of casual collectors. This quarter has an error on the back, where the ear of corn is shown. Some of these coins have an “extra leaf” that shouldn’t be there. There are two kinds:
- “Extra High Leaf”: The extra leaf is higher up on the corn.
- “Extra Low Leaf”: The extra leaf is lower down on the corn.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| Circulated | $50 – $150 |
| Uncirculated (MS-60) | $150 – $300 |
| High Grade (MS-65+) | $300 – $1,000+ |
How much is a quarter worth may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors
1999 Delaware “Spitting Horse” Quarter

Many old quarters worth money gain value due to their age and errors. Look closely at the horse on the back of the 1999 Delaware quarter. Some of these coins have a small, raised line or “cud” coming from the horse’s mouth, making it look like it’s spitting.
This is a die break error. It means a tiny piece of the metal die broke off, creating that extra mark on the coin.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| Circulated | $10 – $30 |
| Uncircated (MS-60) | $30 – $70 |
| High Grade (MS-65+) | $70 – $200+ |
Rare quarters worth money may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors
2005-P Minnesota Quarter: Doubled Dies
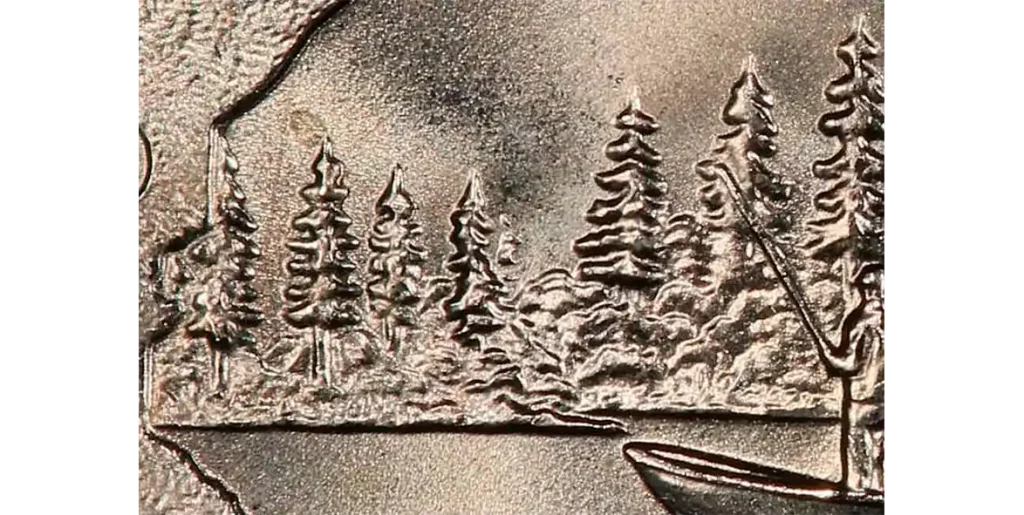

For the 2005-P Minnesota quarter, you need to look at the outline of the state on the back. Some of these coins show a doubled die error. This means parts of the design, like the state outline or some trees, look slightly blurry or doubled.
This happens when the coin die is stamped more than once, but not perfectly aligned, making the image appear like a slight shadow.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| Circulated | $5 – $25 |
| Uncirculated (MS-60) | $25 – $75 |
| High Grade (MS-65+) | $75 – $200+ |
Quarters that are worth money may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors
2007 Wyoming Quarter: Cracked Die “Bison Horn” Errors

This error takes place near the bucking horse. Cracked die means a small piece of the coin’s die broke off. When the coin was made, this broken part caused a raised, uneven line or bump on the horse’s head or horn. It looks like an extra horn or a strange shape on the horse’s head.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| Circulated | $5 – $20 |
| Uncirculated (MS-60) | $20 – $50 |
| High Grade (MS-65+) | $50 – $150+ |
Which quarters are worth money may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors
State Quarters That Outperform
Pennsylvania (1999): Experimental alloy coins like Georgia

These quarters might look slightly different in color, sometimes having a more golden or greenish tint compared to a regular quarter. They might also feel a bit different or even have a slightly different weight or a smooth edge. The key is that their metal make-up is not the standard copper-nickel.
The exact composition of these experimental alloy 1999 Pennsylvania Quarters can vary, but generally they are:
- Copper: 69% to 77%
- Zinc: 12% to 27%
- Manganese: 1.6% to 7%
- Nickel: 2% to 4%
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| MS60 (Uncirculated) | $500 – $1,500+ |
| MS64 (Nice Uncirculated) | $1,500 – $3,000+ |
| MS67 (Very High Grade) | $5,000 – $10,000+ |
How much is a silver quarter worth may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors
Kansas (2005): “In God We Rust” grease errors

On the front side of the coin, in the motto “IN GOD WE TRUST,” the “T” in “TRUST” might be partly or completely missing, making it look like “IN GOD WE RUST.” This happens when a small amount of grease, dirt, or metal dust gets stuck on the coin die. When the die presses onto the blank coin, the grease fills in part of the design, so that part doesn’t get stamped clearly onto the coin.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| AU50 (About Uncirculated) | $50 – $150 |
| MS60 (Uncirculated) | $100 – $300 |
| MS65 (Nice Uncirculated) | $300 – $1,000+ |
| MS67 (Very High Grade) | $2,000 – $5,000+ |
What year quarters are worth money may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors
Nevada (2006): Missing clad layer two-tone errors

On the coin with a missing clad layer, one or both of these outer layers did not bond properly to the copper core and came off. This leaves the coin looking two-toned, with a reddish-brown copper color on one side and the normal silvery color on the other. Sometimes, the missing layer can be only a small part of the coin, or it can be the entire side.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| XF (Extra Fine) | $50 – $200 |
| AU (About Uncirculated) | $100 – $350 |
| MS60 (Uncirculated) | $200 – $500 |
| MS64 (Nice Uncirculated) | $300 – $800+ |
| MS66 (High Grade) | $800 – $2,000+ |
How much are silver quarters worth may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors
Modern Rarities (2010-2024)
National Park Quarters: 2010 Hot Springs Arkansas

A regular 2010 Hot Springs quarter is common. But a coin that has no marks, no scratches, and perfect shine is very rare. We are talking about coins that have been kept in special ways, never touched by hands, and never put into circulation.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| MS67 (Very High Grade) | $50 – $150 |
| MS68 (Even Higher Grade) | $150 – $500 |
| MS69 (Nearly Perfect) | $700 – $1,500+ |
| MS70 (Perfect) | $1,500 – $3,000+ |
How much are quarters worth may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors
American Women Series: 2022 Maya Angelou (MS67+: $2,735)

The 2022 Maya Angelou quarter can be very valuable when it has a high-grade error, specifically a die crack, or if it’s in a perfect condition. This happens when the metal die that stamps the coin starts to break. The crack then shows up as a raised line on the coin itself. These errors are more common than other, but a clear distinct die crack can add value.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| MS60 (Uncirculated) | $1 – $5 |
| MS65 (Nice Uncirculated) | $5 – $20 |
| MS67 (Very High Grade) | $20 – $1000 |
| MS67+ (Exceptional) | $100 – $3000+ |
| MS68 (Near Perfect) | $500 – $3,500+ |
| MS69 (Perfect) | $2,000 – $5,000+ |
What year of quarters are worth money may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors
2023 Jovita Idar Quarter: Look for Doubled Die Errors
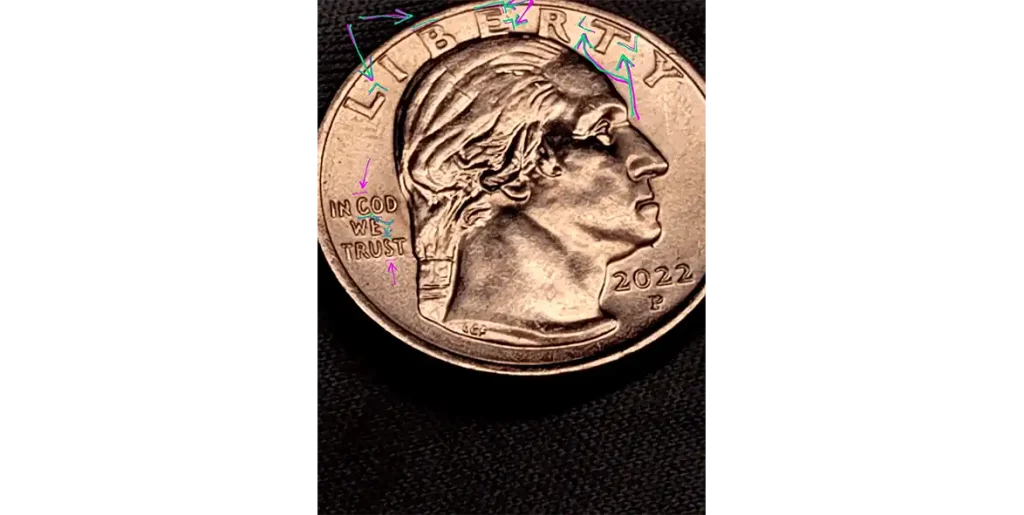

Some 2023 Jovita Idar quarters have a doubled die error. This means parts of the design on the front side of the coin appear slightly doubled or blurry. Carefully check the lettering and details on the “heads” side of the coin. You might see that letters or numbers look like they were stamped twice, slightly offset. This happens when the die itself has a small mistake, causing part of the design to be impressed more than once in slightly different spots.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| AU50 (About Uncirculated) | $20 – $75 |
| MS60 (Uncirculated) | $50 – $150 |
| MS64 (Nice Uncirculated) | $100 – $300 |
| MS66 (High Grade) | $250 – $800+ |
| MS67+ (Very High Grade) | $500 – $1,500+ |
How much is a gold quarter worth may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors
How to Identify Rare Quarters
Learning how to know if your quarter is worth money involves checking for errors and specific dates:
- Check the Date and Mint Mark. First, look at the year the quarter was made. Also, find the small letter on the coin. This is the “mint mark” and it tells you where the coin was produced. Quarters made before 1965 are special because they contain silver. Silver is worth more than the regular metals used in quarters today. Some quarters have a “W” for West Point or an “S” for San Francisco as their mint mark. These are often made in smaller numbers or are special collector coins. For example, some 2020 quarters with a “W” mint mark are very rare.
- Look for Errors. Look for extra details on the coin that shouldn’t be there. You can tell what quarter is worth money if it has an “extra leaf” error or something else. Sometimes, a part of the design might be missing or look very weak. This can happen if dirt or grease gets on the machine that stamps the coin. For example, some coins might have a word that looks like it’s missing a letter. Very rarely, a coin might be made on the wrong type of metal. This makes it look different in color or weight from a normal quarter. You might see parts of the letters or numbers looking a bit blurry or like they are doubled. This is called a “doubled die” error.
- How Good Does It Look. A coin that looks like it was just made, with no scratches or wear, is worth much more than a worn-out coin. Collectors call these “uncirculated” coins. If you think you have a very valuable quarter, you can send it to special companies or use special apps. It will check the coin very carefully and give it a grade.
For youth generation here are a lot of hobbies instead of be interested in how much is a quarter of weed worth. Hobbies like collecting coins can teach you about rare things, how to pay attention to small details, and how markets work.